Stable Diffusion 硬核生存指南:WebUI 中的 GFPGAN (二)
本篇文章聊聊 Stable Diffusion WebUI 中的核心组件,强壮的人脸图像面部画面修复模型 GFPGAN 相关的事情。
GFPGAN 代码执行逻辑
GFPGAN 的模型执行逻辑,简单来说和 CodeFormer 类似,也是读取图片,分析人脸使用模型进行处理、替换原图中的人脸,保存图片。
模型的加载和使用逻辑
在 TencentARC/GFPGAN/gfpgan/utils.py[14] 文件中,定义了 GFPGANer 工具类,包含了主要的流程逻辑,默认提取并处理图像中的面部,然后将图片尺寸调整为 512x512,以及包含了对 GFPGAN 项目发布的各版本模型进行了调用上的兼容性处理。
在创建 GFPGAN 模型实例的时候,我们可以选择三种 GFPGAN 架构的模型:
•clean 适用于第一个版本(v1)模型之外的模型架构,使用 StyleGAN2 Generator 搭配 SFT 模块 (Spatial Feature Transform),这个选项也是程序的默认值,程序文件在 gfpgan/archs/gfpganv1_clean_arch.py[15]。•bilinear 适用于在第三个版本(v1.3)和之后的模型,双线性算法实现,没有复杂的 UpFirDnSmooth,程序文件在 gfpgan/archs/gfpgan_bilinear_arch.py[16]。•original 第一个版本(v1)模型使用的架构,模型文件在 gfpgan/archs/gfpganv1_arch.py[17]
在实际代码定义中,前两种架构的调用参数是一致的,而第三种 original 在参数 fix_decoder 上和前两者数值有差异,为 True。
还有一种全新的架构:RestoreFormer。这种架构就是我们第一篇硬核生存指南中提到的《Stable Diffusion 硬核生存指南:WebUI 中的 VAE[18]》,相关程序文件在 gfpgan/archs/restoreformer_arch.py[19]
在面部恢复过程中,还会使用到上一篇文章中提到的 facexlib 项目中的 retinaface_resnet50 模型,来对图片进行恢复和保存。
下面是简化后的程序,包含了 GFPGAN 的处图片理流程:
import cv2
import torch
from basicsr.utils import img2tensor, tensor2img
from torchvision.transforms.functional import normalize
class GFPGANer():
"""Helper for restoration with GFPGAN.
Args:
model_path (str): The path to the GFPGAN model. It can be urls (will first download it automatically).
upscale (float): The upscale of the final output. Default: 2.
arch (str): The GFPGAN architecture. Option: clean | original. Default: clean.
channel_multiplier (int): Channel multiplier for large networks of StyleGAN2. Default: 2.
bg_upsampler (nn.Module): The upsampler for the background. Default: None.
"""
def __init__(self, model_path, upscale=2, arch='clean', channel_multiplier=2, bg_upsampler=None, device=None):
self.upscale = upscale
self.bg_upsampler = bg_upsampler
...
self.gfpgan = self.gfpgan.to(self.device)
@torch.no_grad()
def enhance(self, img, has_aligned=False, only_center_face=False, paste_back=True, weight=0.5):
self.face_helper.clean_all()
if has_aligned: # the inputs are already aligned
img = cv2.resize(img, (512, 512))
self.face_helper.cropped_faces = [img]
else:
self.face_helper.read_image(img)
# get face landmarks for each face
self.face_helper.get_face_landmarks_5(only_center_face=only_center_face, eye_dist_threshold=5)
# eye_dist_threshold=5: skip faces whose eye distance is smaller than 5 pixels
# TODO: even with eye_dist_threshold, it will still introduce wrong detections and restorations.
# align and warp each face
self.face_helper.align_warp_face()
# face restoration
for cropped_face in self.face_helper.cropped_faces:
# prepare data
cropped_face_t = img2tensor(cropped_face / 255., bgr2rgb=True, float32=True)
normalize(cropped_face_t, (0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5), inplace=True)
cropped_face_t = cropped_face_t.unsqueeze(0).to(self.device)
try:
output = self.gfpgan(cropped_face_t, return_rgb=False, weight=weight)[0]
# convert to image
restored_face = tensor2img(output.squeeze(0), rgb2bgr=True, min_max=(-1, 1))
except RuntimeError as error:
print(f'\tFailed inference for GFPGAN: {error}.')
restored_face = cropped_face
restored_face = restored_face.astype('uint8')
self.face_helper.add_restored_face(restored_face)
if not has_aligned and paste_back:
# upsample the background
if self.bg_upsampler is not None:
# Now only support RealESRGAN for upsampling background
bg_img = self.bg_upsampler.enhance(img, outscale=self.upscale)[0]
else:
bg_img = None
self.face_helper.get_inverse_affine(None)
# paste each restored face to the input image
restored_img = self.face_helper.paste_faces_to_input_image(upsample_img=bg_img)
return self.face_helper.cropped_faces, self.face_helper.restored_faces, restored_img
else:
return self.face_helper.cropped_faces, self.face_helper.restored_faces, None
在 GFPGANer 初始化完毕后,就可以调用 enhance 方法,来对图片进行画面增强了,依次会清理之前任务的战场、判断图片是否已经对齐,如果是已经对齐的图片,则直接将扣出来的人脸区域传递给下一个流程,如果尚未进行图片对齐,则读取图片然后获取所有的人脸区域。
接着依次将每一张人脸画面传递给 GFPGAN 模型进行处理,将处理后的结果使用 tensor2img 转换回图片,接着将处理好的人脸图像区域粘贴回原始图片。
这里如果用户设置了背景采样器,则会调用相关模型方法处理背景。整体上和 CodeFormer 的流程差不多。
模型训练
在项目的 gfpgan/train.py[20] 程序中,包含了训练模型的入口。
执行程序实际会调用 gfpgan/models/gfpgan_model.py[21] 文件进行模型训练,这部分不是本文重点,和 WebUI 关联性不大就不展开了。
Stable Diffusion WebUI 中的调用逻辑
在 WebUI 程序入口 webui.py[22] 程序中,能够看到 GFPGAN 在程序初始化时进行了模型的加载,在 SD 主要绘图模型和上一篇文章提到的 CodeFormer 初始化之后:
def initialize():
...
modules.sd_models.setup_model()
startup_timer.record("setup SD model")
codeformer.setup_model(cmd_opts.codeformer_models_path)
startup_timer.record("setup codeformer")
...
gfpgan.setup_model(cmd_opts.gfpgan_models_path)
startup_timer.record("setup gfpgan")
...上一篇文章中,CodeFormer 只能够通过一个参数来改变加载行为,到了 GFPGAN 后,我们能够使用的参数增加到了四个:
parser.add_argument("--gfpgan-dir", type=str, help="GFPGAN directory", default=('./src/gfpgan' if os.path.exists('./src/gfpgan') else './GFPGAN'))
parser.add_argument("--gfpgan-model", type=str, help="GFPGAN model file name", default=None)
parser.add_argument("--unload-gfpgan", action='store_true', help="does not do anything.")
parser.add_argument("--gfpgan-models-path", type=str, help="Path to directory with GFPGAN model file(s).", default=os.path.join(models_path, 'GFPGAN'))程序在启动过程中,会调用 modules/launch_utils.py[23] 程序中的 prepare_environment 来准备组件代码:
def prepare_environment():
...
gfpgan_package = os.environ.get('GFPGAN_PACKAGE', "https://github.com/TencentARC/GFPGAN/archive/8d2447a2d918f8eba5a4a01463fd48e45126a379.zip")
...
if not is_installed("gfpgan"):
run_pip(f"install {gfpgan_package}", "gfpgan")
...这里使用的版本,其实是 v1.3.5 版本后发布的一个临时提交 “update cog predict[24]”,而在项目的 requirement 依赖声明文件中,我们能够看到项目会使用 1.3.8 版本的 GFPGAN。
当然,这个代码只会在本地依赖缺失的时候执行,但考虑到一致性,我们可以将其更新,改为相同版本,这里我提交了一个版本修正的 PR[25],如果作者合并之后,这个不一致的潜在问题就没有啦。
类似的,在模块程序 modules/gfpgan_model.py[26] 中,定义了使用 GFPGAN 的图片处理过程,和上文中的处理逻辑也是一致的:
import modules.face_restoration
from modules import shared
def gfpgann():
return model
def send_model_to(model, device):
model.gfpgan.to(device)
model.face_helper.face_det.to(device)
model.face_helper.face_parse.to(device)
def gfpgan_fix_faces(np_image):
return np_image
gfpgan_constructor = None
def setup_model(dirname):
def my_load_file_from_url(**kwargs):
return load_file_from_url_orig(**dict(kwargs, model_dir=model_path))
def facex_load_file_from_url(**kwargs):
return facex_load_file_from_url_orig(**dict(kwargs, save_dir=model_path, model_dir=None))
def facex_load_file_from_url2(**kwargs):
return facex_load_file_from_url_orig2(**dict(kwargs, save_dir=model_path, model_dir=None))
class FaceRestorerGFPGAN(modules.face_restoration.FaceRestoration):
def name(self):
return "GFPGAN"
def restore(self, np_image):
return gfpgan_fix_faces(np_image)
shared.face_restorers.append(FaceRestorerGFPGAN())不过,默认的加载模型是 v1.4 版本,如果你有风格上的指定速度,或许也可以切换到 v1.3 版本。
实际调用 GFPGAN 的逻辑在 modules/postprocessing.py[27] 和 scripts/postprocessing_gfpgan.py[28],依旧是依赖后处理脚本执行逻辑。
当然,因为 GFPGAN 和 CodeFormer 在项目中的作用类似,所以存在选择到底使用哪一种方案的选择题,这个模型选择功能,程序文件在 scripts/xyz_grid.py[29]:
def apply_face_restore(p, opt, x):
opt = opt.lower()
if opt == 'codeformer':
...
elif opt == 'gfpgan':
is_active = True
p.face_restoration_model = 'GFPGAN'
else:
...
p.restore_faces = is_activeStable Diffusion WebUI 中 GFPGAN 的额外注意事项
GFPGAN 的模型加载策略比 CodeFormer 写的健壮一些。所以不用担心加载不到模型,整个程序无法使用的问题。不过,它在初始化过程中,也不是没有问题,比如初始化过程中,这个模块会无限挂起(如果遇到网络问题)。
默认程序会查找程序目录下的 gfpgan/weights 的两个模型文件,如果下载不到,就会进行下载:
Downloading: "https://github.com/xinntao/facexlib/releases/download/v0.1.0/detection_Resnet50_Final.pth" to .../gfpgan/weights/detection_Resnet50_Final.pth
Downloading: "https://github.com/xinntao/facexlib/releases/download/v0.2.2/parsing_parsenet.pth" to .../gfpgan/weights/parsing_parsenet.pth这段行为的调用逻辑来自 GFPGAN 中的 gfpgan/utils.py[30]:
from basicsr.utils.download_util import load_file_from_url
...
if model_path.startswith('https://'):
model_path = load_file_from_url(url=model_path, model_dir=os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, 'gfpgan/weights'), progress=True, file_name=None)
loadnet = torch.load(model_path)
...下载函数来自 XPixelGroup/BasicSR/basicsr/utils/download_util.py[31] 程序中,简单封装的 torch.hub 中的方法:
from torch.hub import download_url_to_file, get_dir
def load_file_from_url(url, model_dir=None, progress=True, file_name=None):
"""Load file form http url, will download models if necessary.
Reference: https://github.com/1adrianb/face-alignment/blob/master/face_alignment/utils.py
Args:
url (str): URL to be downloaded.
model_dir (str): The path to save the downloaded model. Should be a full path. If None, use pytorch hub_dir.
Default: None.
progress (bool): Whether to show the download progress. Default: True.
file_name (str): The downloaded file name. If None, use the file name in the url. Default: None.
Returns:
str: The path to the downloaded file.
"""
if model_dir is None: # use the pytorch hub_dir
hub_dir = get_dir()
model_dir = os.path.join(hub_dir, 'checkpoints')
os.makedirs(model_dir, exist_ok=True)
parts = urlparse(url)
filename = os.path.basename(parts.path)
if file_name is not None:
filename = file_name
cached_file = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(model_dir, filename))
if not os.path.exists(cached_file):
print(f'Downloading: "{url}" to {cached_file}\n')
download_url_to_file(url, cached_file, hash_prefix=None, progress=progress)
return cached_file而 PyTorch 中的 _modules/torch/hub.html#download_url_to_file[32] 方法,实现的也非常简单,不包括任何重试、超时、握手错误等处理逻辑:
def download_url_to_file(url, dst, hash_prefix=None, progress=True):
r"""Download object at the given URL to a local path.
Args:
url (str): URL of the object to download
dst (str): Full path where object will be saved, e.g. ``/tmp/temporary_file``
hash_prefix (str, optional): If not None, the SHA256 downloaded file should start with ``hash_prefix``.
Default: None
progress (bool, optional): whether or not to display a progress bar to stderr
Default: True
Example:
>>> # xdoctest: +REQUIRES(env:TORCH_DOCTEST_HUB)
>>> # xdoctest: +REQUIRES(POSIX)
>>> torch.hub.download_url_to_file('https://s3.amazonaws.com/pytorch/models/resnet18-5c106cde.pth', '/tmp/temporary_file')
"""
file_size = None
req = Request(url, headers={"User-Agent": "torch.hub"})
u = urlopen(req)
meta = u.info()
if hasattr(meta, 'getheaders'):
content_length = meta.getheaders("Content-Length")
else:
content_length = meta.get_all("Content-Length")
if content_length is not None and len(content_length) > 0:
file_size = int(content_length[0])
# We deliberately save it in a temp file and move it after
# download is complete. This prevents a local working checkpoint
# being overridden by a broken download.
dst = os.path.expanduser(dst)
dst_dir = os.path.dirname(dst)
f = tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(delete=False, dir=dst_dir)
try:
if hash_prefix is not None:
sha256 = hashlib.sha256()
with tqdm(total=file_size, disable=not progress,
unit='B', unit_scale=True, unit_divisor=1024) as pbar:
while True:
buffer = u.read(8192)
if len(buffer) == 0:
break
f.write(buffer)
if hash_prefix is not None:
sha256.update(buffer)
pbar.update(len(buffer))
f.close()
if hash_prefix is not None:
digest = sha256.hexdigest()
if digest[:len(hash_prefix)] != hash_prefix:
raise RuntimeError('invalid hash value (expected "{}", got "{}")'
.format(hash_prefix, digest))
shutil.move(f.name, dst)
finally:
f.close()
if os.path.exists(f.name):
os.remove(f.name)所以,在实际使用的过程中,如果存在网络问题,最好预先下载好模型,放在程序读取的到的位置,然后再初始化程序。
另外,在使用 v1 版本最初发布的模型时,如果我们直接在程序中切换使用最初的发布的模型时,会收到类似下面的错误信息:
NameError: name 'fused_act_ext' is not defined
这是因为上文提到的架构不同,除了传递参数有变化之外,我们还需要指定一个环境变量:
BASICSR_JIT=True python app.py
在 Docker 中使用,可以使用下面的命令,将环境变量传递到容器内部:
docker run --gpus all --ipc=host --ulimit memlock=-1 --ulimit stack=67108864 --rm -it -e BASICSR_JIT=True -v `pwd`/model:/app/model -v `pwd`/gfpgan:/app/gfpgan -p 7860:7860 soulteary/docker-gfpgan
想比较直接执行,这里会进行 CUDA 插件的编译,所以会需要额外的时间,完成之后,我们熟悉的界面将多两个选项: “v1” 版本的模型和 RealESR GAN 的“v2” 版本,这是项目最初发布时的组合。
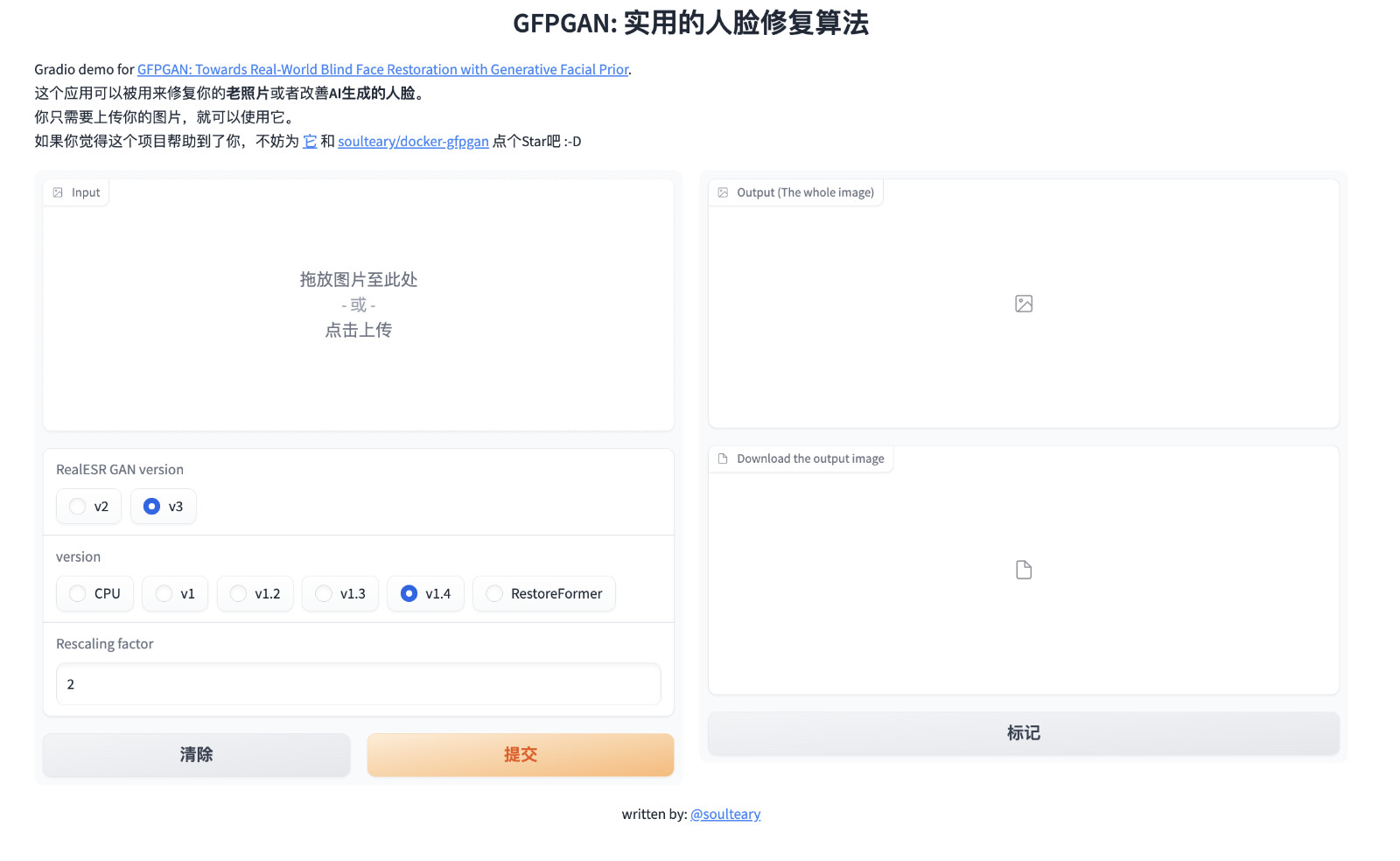
还有几个不影响实际使用的小问题。在安装准备环境过程中因为子依赖版本冲突,报错的问题,因为我们实际代码没有依赖和使用 google-auth-oauthlib 相关功能,可以暂时忽略这个问题:
ERROR: pip's dependency resolver does not currently take into account all the packages that are installed. This behaviour is the source of the following dependency conflicts.
tensorboard 2.9.0 requires google-auth-oauthlib<0.5,>=0.4.1, but you have google-auth-oauthlib 1.0.0 which is incompatible.
tensorboard 2.9.0 requires tensorboard-data-server<0.7.0,>=0.6.0, but you have tensorboard-data-server 0.7.1 which is incompatible.最后
本篇文章就先写到这里吧,下一篇文章再见。
–EOF
本文使用「署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0)」许可协议,欢迎转载、或重新修改使用,但需要注明来源。 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0)
本文作者: 苏洋
创建时间: 2023年08月04日 统计字数: 19172字 阅读时间: 39分钟阅读 本文链接: https://soulteary.com/2023/08/04/stable-diffusion-hardcore-survival-guide-gfpgan-in-webui.html
引用链接
[14] TencentARC/GFPGAN/gfpgan/utils.py: https://github.com/TencentARC/GFPGAN/blob/master/gfpgan/utils.py[15] gfpgan/archs/gfpganv1_clean_arch.py: https://github.com/TencentARC/GFPGAN/blob/master/gfpgan/archs/gfpganv1_clean_arch.py[16] gfpgan/archs/gfpgan_bilinear_arch.py:[17] gfpgan/archs/gfpganv1_arch.py: https://github.com/TencentARC/GFPGAN/blob/master/gfpgan/archs/gfpganv1_arch.py[18] Stable Diffusion 硬核生存指南:WebUI 中的 VAE: https://soulteary.com/2023/07/30/stable-diffusion-hardcore-survival-guide-vae-in-webui.html[19] gfpgan/archs/restoreformer_arch.py: https://github.com/TencentARC/GFPGAN/blob/master/gfpgan/archs/restoreformer_arch.py[20] gfpgan/train.py: https://github.com/TencentARC/GFPGAN/blob/master/gfpgan/train.py[21] gfpgan/models/gfpgan_model.py: https://github.com/TencentARC/GFPGAN/blob/master/gfpgan/models/gfpgan_model.py[22] webui.py: https://github.com/AUTOMATIC1111/stable-diffusion-webui/blob/master/webui.py[23] modules/launch_utils.py: https://github.com/AUTOMATIC1111/stable-diffusion-webui/blob/master/modules/launch_utils.py[24] update cog predict: https://github.com/TencentARC/GFPGAN/commit/8d2447a2d918f8eba5a4a01463fd48e45126a379[25] 一个版本修正的 PR: https://github.com/AUTOMATIC1111/stable-diffusion-webui/pull/12252[26] modules/gfpgan_model.py: https://github.com/AUTOMATIC1111/stable-diffusion-webui/blob/master/modules/gfpgan_model.py[27] modules/postprocessing.py: https://github.com/AUTOMATIC1111/stable-diffusion-webui/blob/master/modules/postprocessing.py[28] scripts/postprocessing_gfpgan.py: https://github.com/AUTOMATIC1111/stable-diffusion-webui/blob/master/scripts/postprocessing_gfpgan.py[29] scripts/xyz_grid.py: https://github.com/AUTOMATIC1111/stable-diffusion-webui/blob/master/scripts/xyz_grid.py[30] gfpgan/utils.py: https://github.com/TencentARC/GFPGAN/blob/master/gfpgan/utils.py[31] XPixelGroup/BasicSR/basicsr/utils/download_util.py: https://github.com/XPixelGroup/BasicSR/blob/master/basicsr/utils/download_util.py[32] _modules/torch/hub.html#download_url_to_file: https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/_modules/torch/hub.html#download_url_to_file
如果你觉得内容还算实用,欢迎点赞分享给你的朋友,在此谢过。
如果你想更快的看到后续内容的更新,请戳 “点赞”、“分享”、“喜欢” ,这些免费的鼓励将会影响后续有关内容的更新速度。